Open Application Programming Interfaces (API): Purpose and Possibilities
by Abhinav Sinha, Piyush Singh, Priya Garg and Anil Gupta
Jun 4, 2016
4 min
Going by the global experience, a set of open, well-documented Application Programming Interface or APIs provide enormous benefits to providers and clients. They also help improve customer experience.
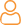
Application Programming Interface or API, a software programme, acts as a bridge between disparate applications. It performs the intended function when a set of instructions are provided through a user interface (UI). The front-end of UI is usually a website or mobile application.
The following diagram illustrates the basic architecture of any API-based business model:
Guided by the strategy of Open APIs, many companies like PayPal, Master card, Mobikwik, M-PESA, Eko, etc. have embarked on this journey for mobile money and payment services. Though a provider charges a fee for consuming APIs, it makes sense to a variety of user organisations on the basis of time-to-market and cost parameters. For many upcoming organisations, it is more feasible to use open APIs of a specialised company, in a particular service line, instead of building the same.
The second generation platform of M-PESA in Kenya allows partners to build on disbursements and services payments like automated payment receipt processing, payment disbursement, and payment reversals in case of failed transactions.
DBS, a Singapore-based bank, has announced a mobile-only bank in India. The digital bank would use open APIs to acquire, authenticate, and facilitate transactions for customers, using Aadhaar.
As part of Digital India, India Stack is a set of open APIs authorised by the government to create an identification, authentication, and transaction ecosystem across different sources. For payment solutions, National Payment Council of India (NPCI) has released its API for Unified Payment Interface (UPI).
| Case Study – Eko’s Open API Platform
Eko India Financial Services is involved in the payments sector with a pre-paid instrument (PPI) licence* from RBI. Eko’s key customers include low- / middle-income customers and micro entrepreneurs earning less than Rs. 50,000 (US$ 770) per month. Eko provides technology platform for bill and merchant payments, peer-to-peer fund transfer, and agent-assisted remittancesEko provides open APIs to organisations interested in money transfer, and charges a fee for using its services and APIs. Eko’s open APIs allow partner entities to leverage Eko’s technology platform and connect with NPCI, UIDAI, banks, and aggregators, to build their own products. So far, Eko has released APIs for its domestic money transfer (DMT) business. This allows others to build their business models by consuming these APIs within the allowed boundary conditions. Besides providing superior UI/UX to their customers, partners have developed innovative payment and financial services use cases such as lending, money transfer, P2P transfers, and in-store and online payments.Open APIs have benefitted both Eko and its partners. Eko’s partners are able to scale rapidly and increase their distribution footprint. Through partners, Eko has been able to reach newer geographies. Eko is planning to expand its partner base, as well as introduce new APIs to provide more services through its ecosystem.The diagram below shows how Eko’s open API interacts with other embedded APIs to complete a money transfer transaction. |
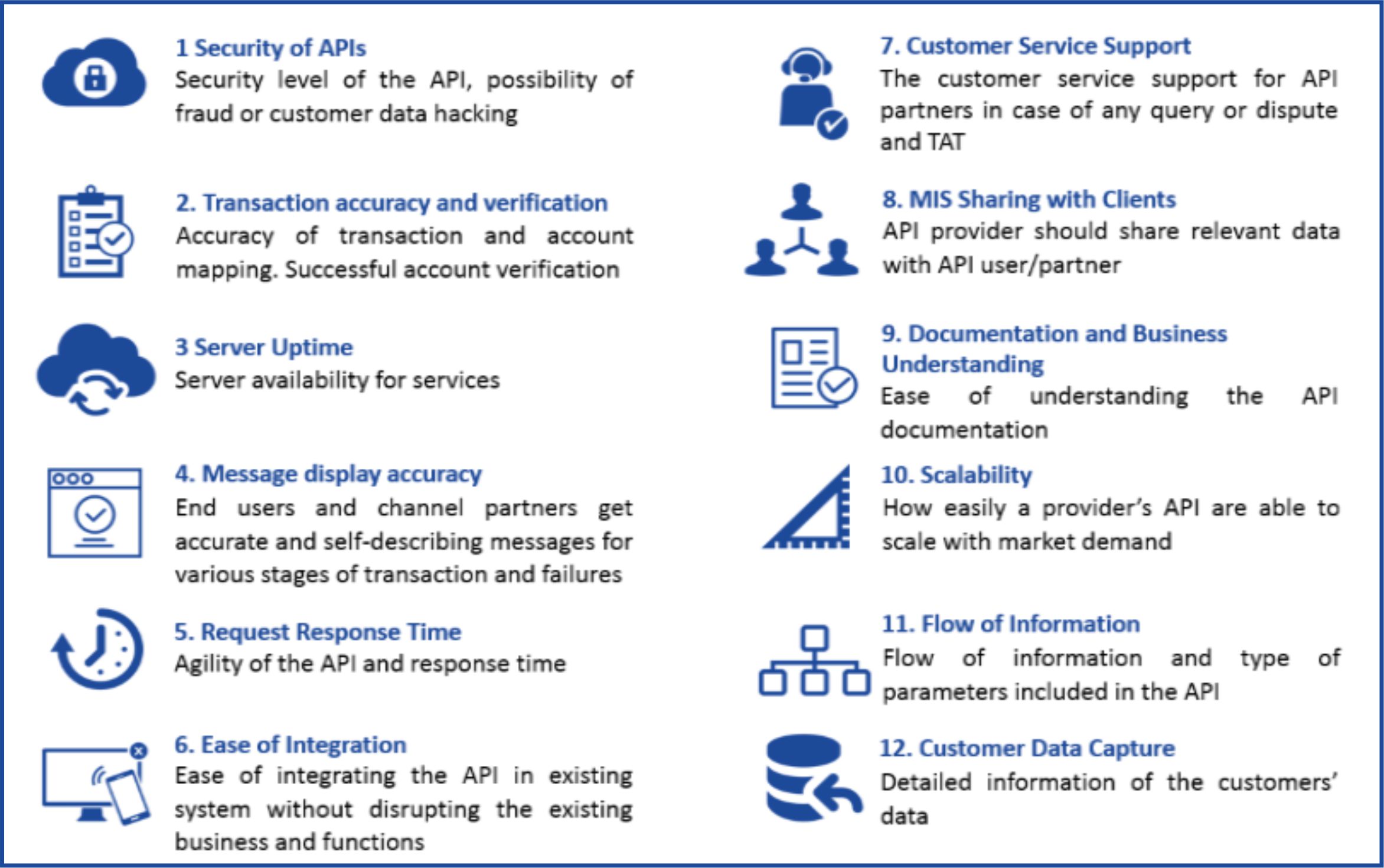
CGAP has identified comprehensive documentation, stability, easy access, and tracking as important elements for success of open API ecosystems. Based on a recent study done by MicroSave on use of APIs with a client, users evaluate the effectiveness of the APIs based on the following parameters:
Benefits of open API
Properly designed APIs provide benefits to both providers and users, along with a positive impact on customers.

• New revenue stream: Providers can capitalise on their existing assets, i.e. software and hardware, by providing their APIs to other companies on payment of a fee.
• Increased outreach: They can reach out to a larger customer base, through partners, without incurring high costs of distribution.
• Better utilisation: Providers can use their hardware effectively and can reap benefit of economies of scale.
• Future proofing: It is difficult to accurately predict the future. Open APIs can help providers a piece of the pie, even on unknown trends, as highlighted by CGAP based on M-PESA’s open APIs.
b) Clients (API Users):
• Time and cost reduction: A significant reduction in the time for go-to-market can be seen by riding on the existing stable platform, instead of developing the complex software. The users can not only reduce the cost of development, but also avoid sinking high one-time capital cost towards hardware.
• Scalability: Instead of worrying on scaling up of software and hardware, the clients can focus on distribution and scale quickly.
• Innovative solution: The clients have to build on the basic APIs exposed by the providers. This enables them to design and provide innovative solutions on top of the basic services provided by the API provider. Such customised solutions can provide unique services and experience to users, in line with local needs.
c) Impact on Customers:
• Convenience and experience: Properly designed and tailored services made available at the doorstep of citizens translates into convenience, and better experience. Even marginalised consumers will be able to choose providers and consume digital services according to their need.
Conclusion
Going by the global experience, a set of open, well-documented APIs provide enormous benefits to providers and clients. They also help improve customer experience.
API providers need to ensure easier integration, customer support, and scalability, while maintaining the security of financial transactions. Clients need to be sure of antecedents and capabilities of service providers as they scale up their businesses.
Today, there is tremendous amount of innovation around open APIs. The Government of India has taken early steps to fuel it through its ambitious Digital India plan. The possibilities of open APIs will only be limited by creativity, imagination, and business requirements.
Abhinav Sinha is co-founder, Eko Financial Services Pvt. Ltd
 by
by 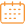 Jun 4, 2016
Jun 4, 2016 4 min
4 min 





Leave comments