How can financial institutions use digital transformation to help MSMEs recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic?
 by Anup Singh and Graham Wright
by Anup Singh and Graham Wright Apr 21, 2021
Apr 21, 2021 6 min
6 min
This blog focus on how financial institutions can use digital transformation to help MSMEs recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic has left micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) decapitalized. With nowhere to turn for reasonably priced credit to reboot their businesses, many will likely be forced to shut down.
Though MSMEs contribute significantly to the economy and employment, they face severe challenges in access to formal financial services. The COVID-19 crisis has exacerbated this lack of access.
In May, 2020, at the peak of the pandemic, only 22% of the enterprises that MSC surveyed in India, Indonesia, Bangladesh, the Philippines, Uganda, Kenya, and Ghana had managed to access credit from formal financial sources. With the onset of COVID-19, the incomes of MSMEs dropped while their access to credit decreased. Struggling to manage liquidity in the wake of rising household and business expenses, MSMEs continue to dip into their savings.
What are the key constraints that limit the growth of MSMEs?
The illustration below highlights the range of challenges MSMEs face. More than 35% of enterprises rated limited access to financial services as the key constraint that prevents them from growing their businesses.
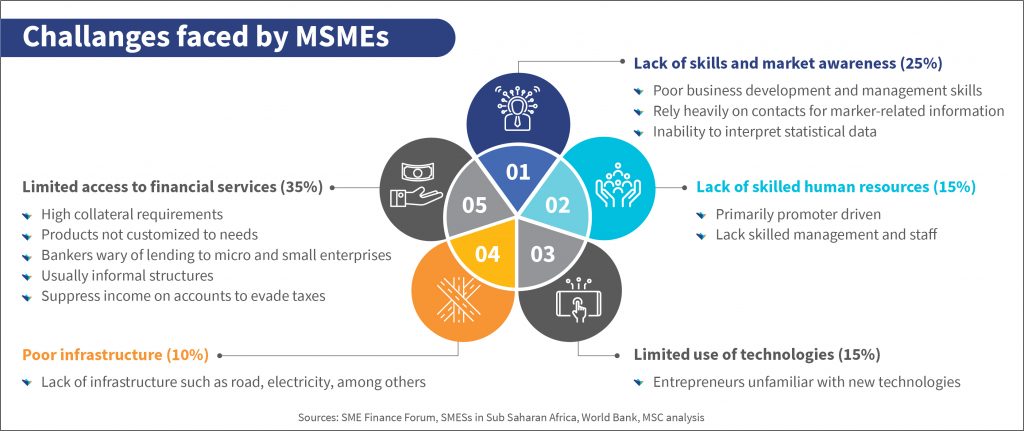
Several studies on the MSME sector suggest that the multiple growth constraints mentioned above can be linked largely to inadequate access to finance. Lack of access to formal credit from financial institutions forces most entrepreneurs to seek funds from family, friends, and informal lenders. Though easily accessible, informal credit comes at prohibitive costs with interest rates of 3–10% per month.
Why do MSMEs have limited access to formal finance?
The reasons for limited access to formal finance for MSMEs are as follows:
- Information asymmetry: The inherent nature of MSMEs is the reason behind the demand-supply gap in access to finance. MSMEs are generally informal and young, have less publicly available information, and operate in unfamiliar sectors. This results in higher information asymmetries and risk, which discourages banks from lending to them.
- Lack of documentation: Most MSMEs do not have enough assets that they can use as collateral. Moreover, financial institutions often require documents, such as certificates of incorporation.
- Process inefficiencies: Most informal enterprises use manual processes, which are costly and inefficient. Process inefficiencies negatively affect record-keeping, cash flow management, and profit optimizing, and compromise loan appraisal metrics by financial services providers.
- Limited digital footprints: Since most MSMEs are informal, the entrepreneur’s profile and business transactions are likely unrepresented or underrepresented in the formal financial ecosystem. This leaves the financial institution with limited digital transactional trails to build a credit score and provide customized financial solutions.
- Perceived as low-return enterprises: Financial institutions do not view MSMEs as a viable target segment compared to large corporate firms. Their perception of MSMEs as high-risk enterprises that offer inadequate returns does not warrant lending to them.
- Inadequate solutions: Limited information and the perception of low returns of MSMEs affect the development of financial services for this sector. This results in none or limited customization of solutions for MSMEs.
- Limited reach to MSMEs: In developing markets, many MSMEs are located outside main market areas. This marginalizes them from the reach of formal financial touchpoints.
How can financial institutions use digital transformation approaches to help MSMEs recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic?
Financial institutions have a clear opportunity to enhance access to finance for MSMEs in emerging economies. Financial institutions may use a multi-pronged approach anchored on digitization to support MSMEs, revive businesses, and build resilience. This will lead to enhanced access to useful, relevant, appropriate, preferred, and used financial solutions for MSMEs delivered using digital tools. The table below summarizes the approach financial institutions can employ to enhance access to finance for MSMEs:
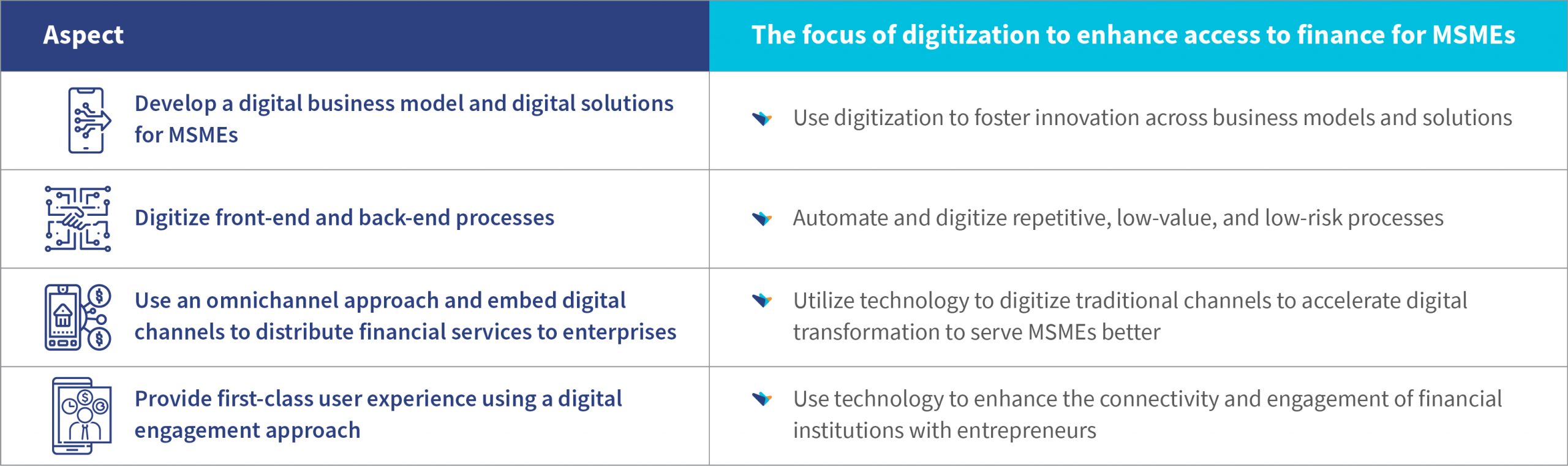
Let us look at each of these aspects in detail.
What digital technologies can financial institutions embed in their business models for MSME finance?
Existing formal financial solutions fail to meet the needs of MSMEs, which presents a significant opportunity for innovation in business models and products. Some approaches to the adoption of innovative business models are as follows:
- Traditional financial institutions that use specialized services in collaboration with service providers, offer technology-driven services, such as credit assessment and risk monitoring, electronic document management, workflow management, digital inventory management and record-keeping, and process automation.
- A focus on enterprises along specific clusters and segments, such as Kopo Kopo in Kenya for mobile money merchants, Neogrowth in India for merchant cash advances, Konfio in Mexico for micro-businesses, and Tienda Pago in Peru for small stores.
- A digital marketplace or platform for financial services, such as SME Corner in India and Yoco in South Africa.
How could financial institutions develop better financial solutions for MSMEs?
Financial institutions can enrich their assessment of client needs, profiles, and segments by better understanding their footprints—digital or potentially digital, to innovate products and services. This data, clubbed with an analysis of behavioral patterns, could lead to hyper-customization of solutions on the go to meet specific needs of MSMEs. Some interesting product-level innovations include digital overdrafts or working capital credit for enterprises, merchant cash advances, invoice discounting within a value or supply chain, receivables financing, and reverse factoring.
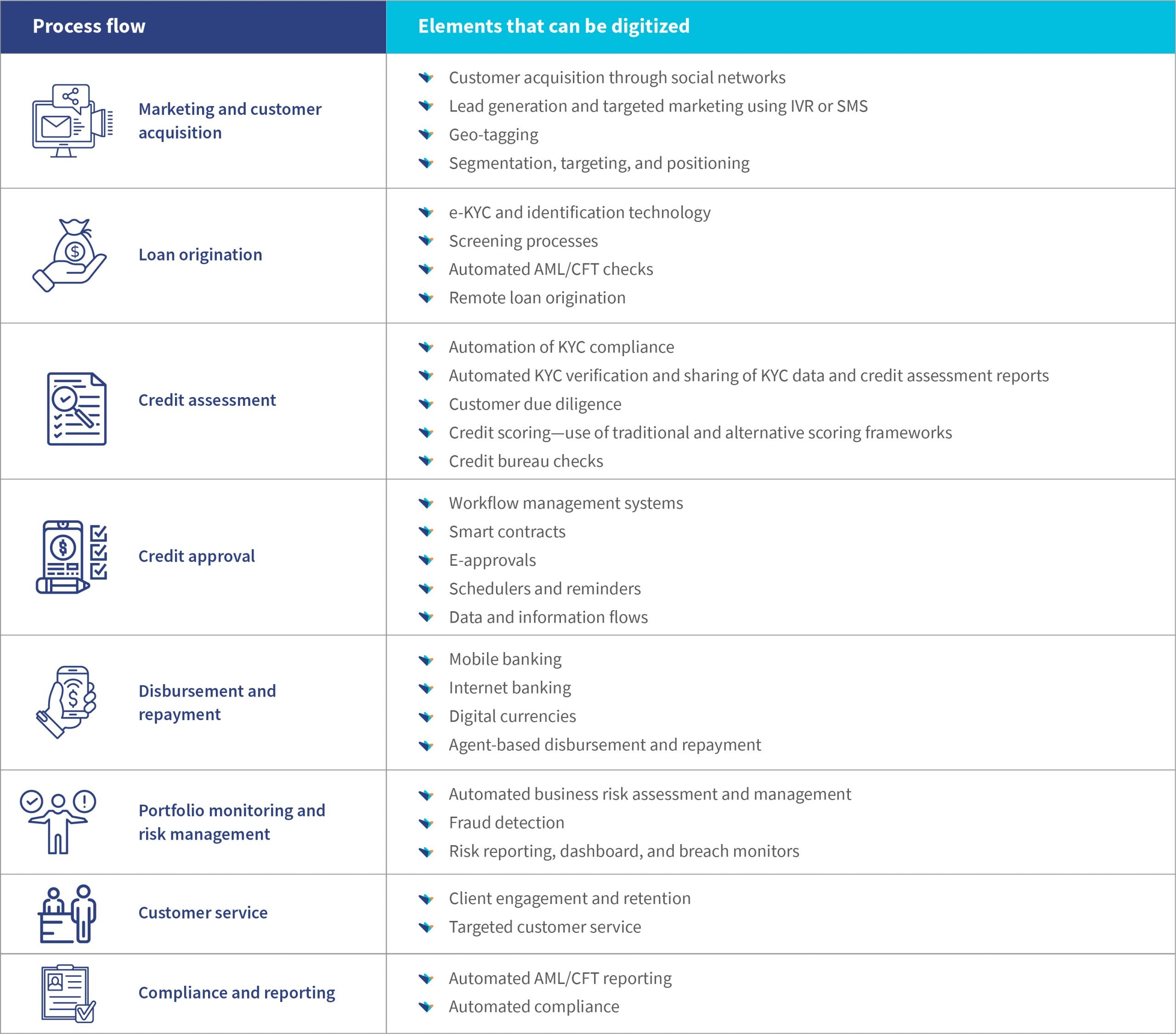
How can financial institutions enhance the efficacy of MSME finance by digitizing processes?
The table below highlights how financial institutions can use digital technologies to enhance efficiency and effectiveness across the process flow.
How could financial institutions use an omnichannel approach and embed digital channels in distribution?
An omnichannel experience involves using technology platforms to improve customer acquisition and user experience while transacting. It allows customers to interact with numerous distribution and delivery channels simultaneously. The emergence of digital platforms and alternative channels has changed the way customers bank. The more access points they have, the better the user experience. Increasingly few customers now want to step into a bank branch.
With the changing market dynamics and preference for more ways to connect and transact, financial institutions need to consider using multiple seamlessly integrated channels to enable entrepreneurs to transact. Despite the complexity of an omnichannel experience, it provides entrepreneurs with a holistic brand experience while financial institutions benefit from the unified view of an entrepreneur. To serve entrepreneurs effectively, financial institutions can use agents, mobile banking applications, internet banking applications, and API-based integrations, besides branches and ATMs.
MSC, through its experience of enabling the digital transformation of financial institutions, has observed that “phygital” models, a combination of physical approaches with the use of digital tools, work better as opposed to an entirely digital model. This is especially the case when users are about to make a decision. A human interface at the point of decision-making reassures users and encourages them to prefer, choose, and use digital financial services confidently. Financial institutions can use trained agents to help entrepreneurs understand solutions and decide which ones to use.
How could financial institutions provide a first-class user experience using a digital engagement approach?
A great user experience involves customer-centric solutions and a manner of delivery that mimics the behaviors and attitudes of users. This ensures that the provision of services is clear, obvious, and intuitive for end-users. To build a customer-centric solution, financial institutions need to focus on user experience, assess bottlenecks that hinder users, incorporate the customer journey approach, embed the progressive learning curve of users, implement design thinking, and personalize user experience.
Financial institutions can utilize digital technology to enhance access to finance for MSMEs. The use of digital technology to enhance access to finance has assumed greater importance since the onset of the pandemic. For this, financial institutions first need to resolve key constraints through the following measures:
- Use alternative data to accurately assess key risks in lending to enterprises and make informed decisions on providing access to finance to MSMEs
- Use cost-effective digital channels to reach MSMEs
- Enhance the efficiency of processes through business process re-engineering and automation to enable a quicker turnaround
- Enhance returns through low-cost, digitally-enabled operations
- Deliver end-user customizable solutions that MSMEs will prefer, chose, and use
- Provide a first-class user experience
Written by

Anup Singh
Associate Director
Leave comments